Results of the first global tap water survey raise big questions on human health
“There are certain commons that connect us all to each other — air, water, soil — and what we have universally found time and time again is if you contaminate any of those commons, it gets in everything.”
Sherri A. Mason, PhD., Chair, Department of Geology and Environmental Sciences,
The State University of New York at Fredonia
Pollutants in the Lifeblood
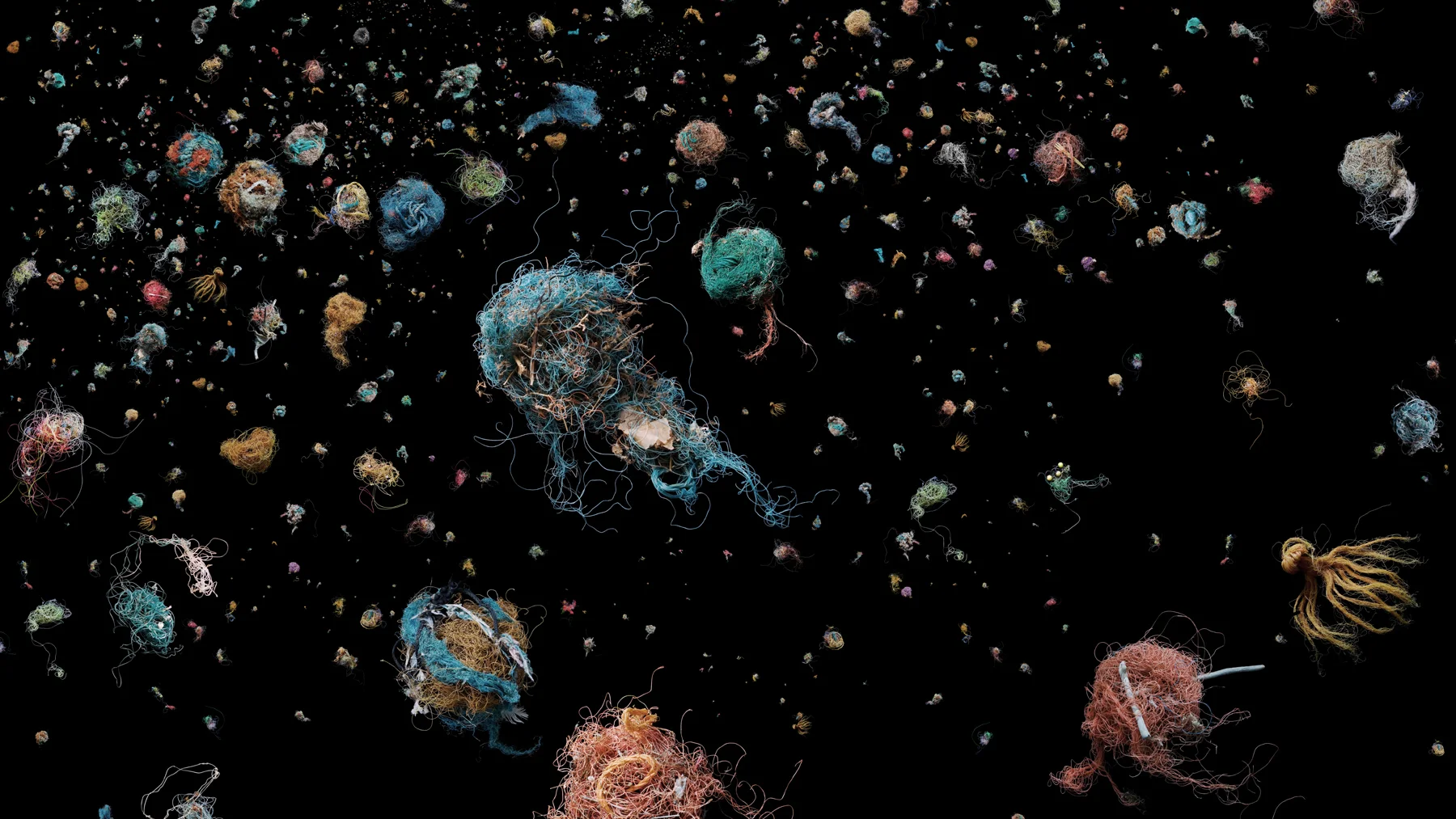
Water is the source, the essential ingredient for life on Earth. Every drop of it that will ever exist on this planet is already here, frozen in ice caps and glaciers or moving in a continuous cycle connecting oceans, atmosphere and biosphere. It courses through our veins and comprises the majority of the human body. We cannot survive without water, yet a material intended to make our lives easier has contaminated it. If you’re drinking tap water, you’re probably ingesting microscopic pieces of plastic.
In a new study by Orb Media, researchers analyzed 159 tap water samples from cities in more than a dozen nations on five continents. Plastic microfibers were found in 83% of those samples. Though shocking, this is just the latest evidence to highlight the enormous complexity and scale of our plastic problems and the dire need for more robust scientific data and analyses on the sources, pathways and toxicity of plastic fibers.
The global survey was conducted by Orb Media in collaboration with researchers at the State University of New York and the University of Minnesota. Findings, which have yet to be peer reviewed, were shared on September 5 via the Guardian and a number of news outlets. Below are a few key numbers:
The US had the highest contamination rate, at 94%, with plastic fibres found in tap water sampled at sites including Congress buildings, the US Environmental Protection Agency’s headquarters, and Trump Tower in New York. Lebanon and India had the next highest rates.
European nations including the UK, Germany and France had the lowest contamination rate at 72%.
The average number of fibers found in each 500ml sample ranged from 4.8 in the US to 1.9 in Europe.
In a separate study released in June, microplastic contamination was found in a handful of tap water and well samples in Ireland. Together with the new report, these findings emphasize the global scale of a growing issue we can't afford to ignore. If plastic fibers are in our water, they’re most likely in the food we make with water, like bread, pasta, soup, and baby formula. It's highly probable they're in our bodies, too.
The Impact on Humans
More research needs to be done to understand the threat and its long-term consequences on human health. One thing revealed in previous studies: microplastics can absorb bacteria and chemical contaminants from surrounding environments. In marine wildlife studies, microplastics have been shown to transfer these harmful chemicals from their plastic hosts onto—or into—tissues, which in turn adversely affects the animals. At a nanometer in size, plastic fibers can penetrate cells, which means they can make their way into organs. The Orb analyses caught particles of more than 2.5 microns in size, or 2,500 times bigger than a nanometre.
Unraveling a Ubiquitous Threat
Just about everywhere researchers have looked, they've found traces of plastic. In the deepest ocean trenches, on the most remote shorelines, in fish, beer, honey and sugar. Tiny fibers fall from the air we breathe in our cities and homes. They enter the natural environment from washing machine effluent and air vents, escape drains as tiny microbeads in body scrubs, and shed from larger pieces of plastic that escape poor or nonexistent waste management systems. When it rains, fibers from car tires are carried along with cigarette butts and plastic litter into public waterways. The problem is virtually ubiquitous and growing by the minute. But there's hope: now we know there's a big problem — and we're capable of creating change to fix it, especially when we work together. Developing successful and cost-effective solutions demands a deeper understanding of the threat. "Scientific research is crucial to understand and solve problems, no other method can do this," says Parley Collaborator Dr. Mark Anthony Browne. "Before we can try to solve a problem the problems need to be clearly defined in terms of the precise environmental, economic and social issues. Often, however, these problems are not properly measured and are confused and conflated."
Among the questions we urgently need to answer next: How many more plastic fibers are these studies missing? What are the impacts on human health? How do the microplastics get into our drinking water in the first place? And what can we do to stop it?
Parley Ocean Plastic Council
In a June 6 workshop during our week-long commemoration of World Oceans Day 2017, held alongside the UN Oceans Conference, leading experts in marine science and plastic pollution came together with members of industry, NGOs and government for the first meeting of the Parley Ocean Plastic Council. Together the group explored the existing spectrum of solutions from a diverse range of perspectives and began to develop a roadmap towards long-term solutions under the Parley AIR Strategy: avoid, intercept, redesign. The meeting set a tone of urgency and unity while underlining the importance of the melding of minds and expertise across multiple disciplines in achieving our mutual aim: the end of marine plastic pollution. Parley founder Cyrill Gutsch will speak during the International Conference on Microplastic Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea hosted in Capri, Italy, in September 2017. Stay tuned for the next meeting of the Ocean Plastic Council.
Learn more:
Guardian article
Cover image by Mandy Barker